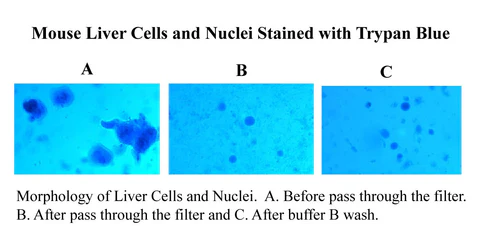
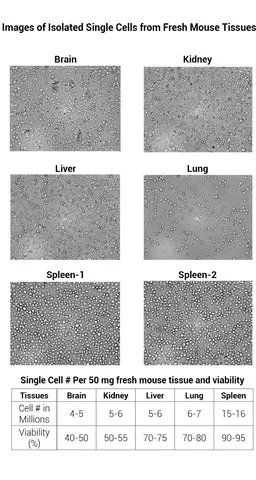
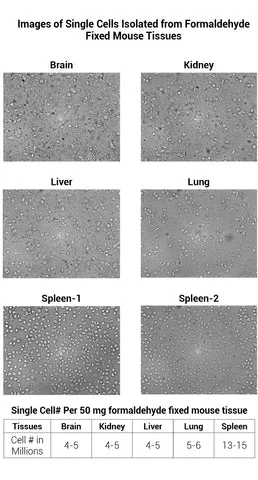
Minute™ Antibody Enhancer (30 ml)
Cat #: WA-002
Description
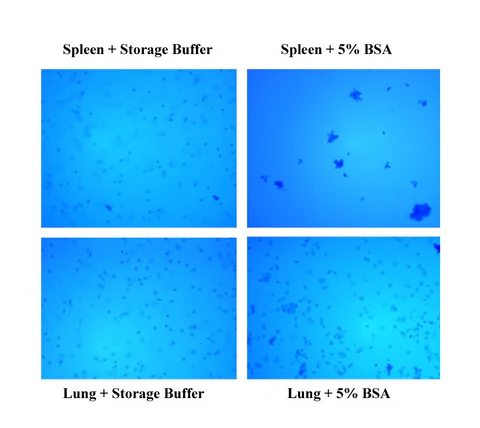
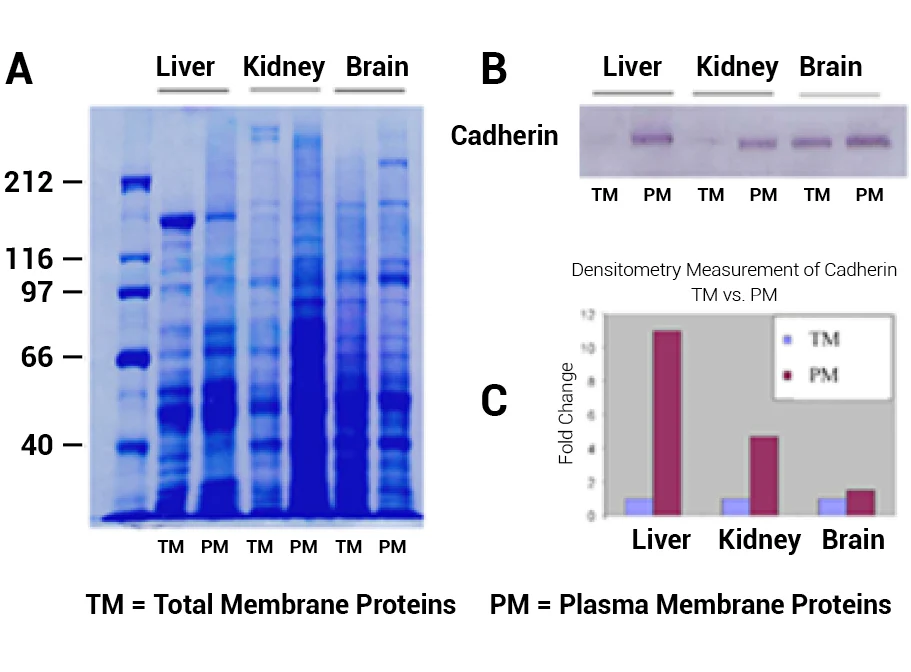
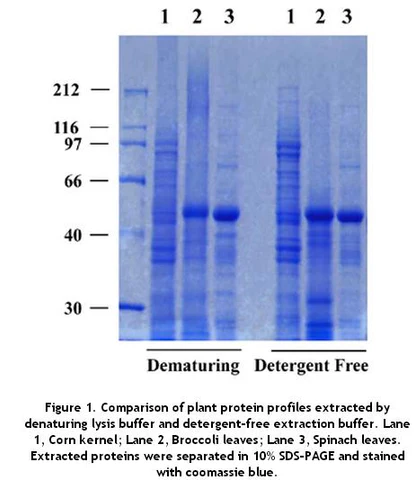
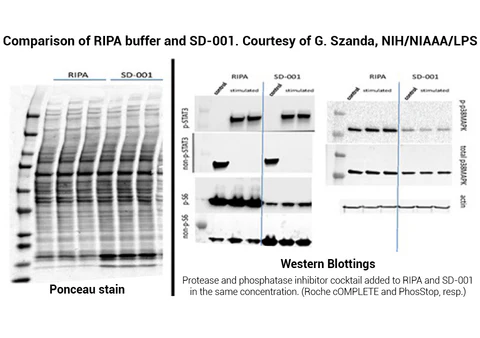
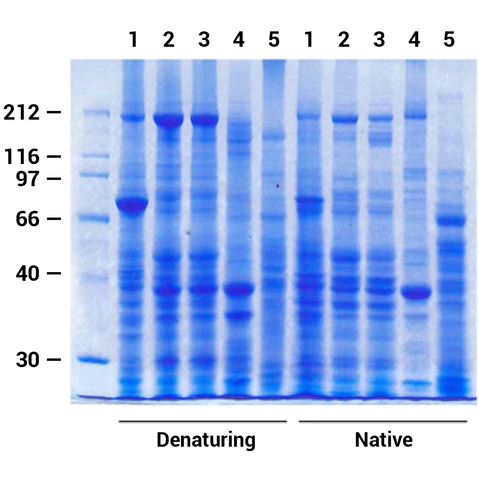
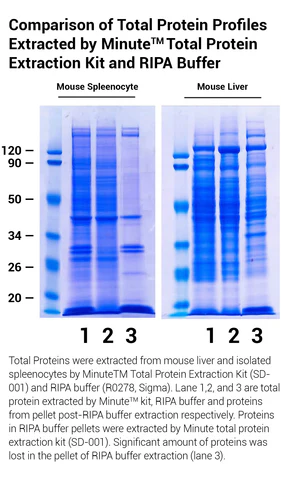
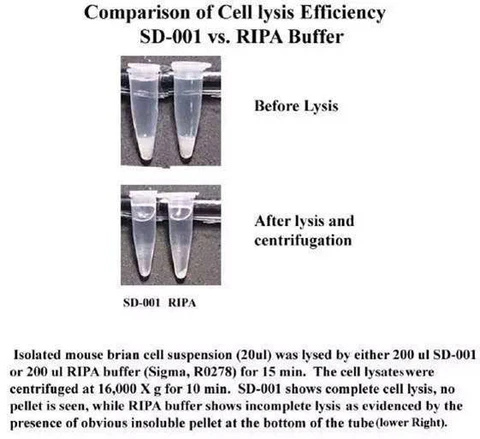
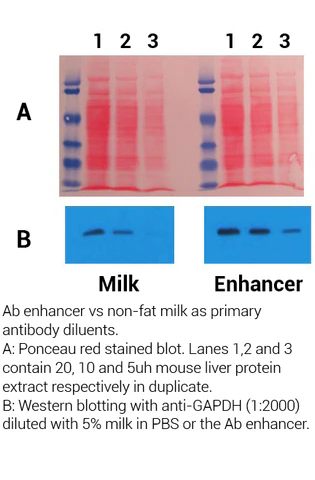
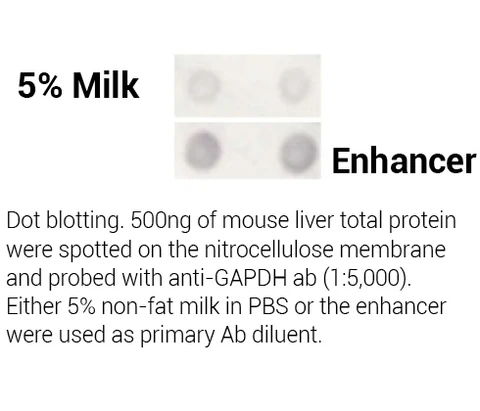
Minute™ Antibody Enhancer is able to significantly increase the sensitivity of commonly used immunoassays such as Western blotting, ELISA and immunohistochemistry. The enhancer can reduce the amount of primary and secondary antibodies used due to higher antibody dilution employed. The signal intensity can be increased in immunostaining applications with chromogenic or fluorescent substrates.
Kit includes:
|
Item |
Quantity |
|
Antibody Enhancer |
30 ml |