


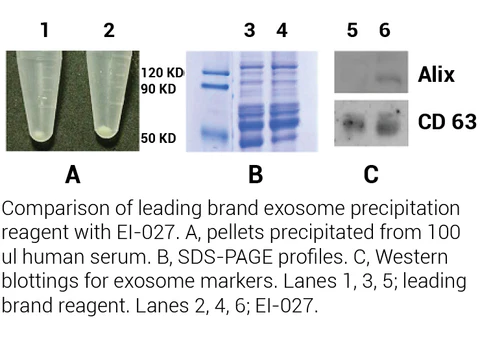
Exosomes are vesicles secreted by cells. They are present in a variety of body fluids such as serum, ascites, spinal cord fluid, urine, and saliva. Cultured cells also secrete significant number of exosomes. The size distribution of exosome is ranging from 30-120 nm. The biological function of exosomes is believed to serve as intercellular messengers. Filtration and ultracentrifugation are classical ways of isolating and enriching exosomes. This is a tedious process and requires special equipment. Another common way for enrichment of exosome is through precipitation. Currently major commercial kits are PEG-based. EI-027 is designed to precipitate total exosomes from biofluids using a high efficacy, non-PEG based reagent for exosome precipitation. This kit is suitable for routine biofluid samples using the same reagent and similar protocol.
Kit includes:
Item | Quantity |
Exosome Precipitation Reagent | 20 ml |
Chen, G., Pu, G., Wang, L., Li, Y., Liu, T., Li, H., … & Luo, X. (2023). Cysticercus pisiformis-derived novel-miR1 targets TLR2 to inhibit the immune response in rabbits. Frontiers in Immunology, 14.